Controllers
Content
Controllers take care of the main interaction between backend and the Twill frontend.
There are many things that can be set and changed.
Controller setup
The main method you will use in a module controller is setupController.
In this method you can set all the options you would like to enable/disable. Keep in mind that for now we only provide methods that change the defaults. This means there might be a disableCreate method, but not a enableCreate as the latter does not change anything and would be redundant.
An example of a setupController call:
1<?php 2 3namespace App\Http\Controllers\Twill; 4 5class ProjectController extends ModuleController 6{ 7 protected $moduleName = 'projects'; 8 9 public function setUpController(): void10 {11 $this->enableShowImage();12 }13}Below is a list of the methods and their purpose:
Disable defaults
- disableCreate: Removes the "Create" button on the listing page.
- disableEdit: Disables table interaction and removes edit links.
- disableSortable: Disables the ability to sort the table by clicking table headers.
- disablePublish: Removes the publish/un-publish icon on the content listing.
- disableBulkPublish: Removes the "publish" option from the bulk operations.
- disableRestore: Removes "restore" from the list item dropdown on the "Trash" content list.
- disableBulkRestore: Removes the "Trash" quick filter.
- disableForceDelete: Removes the "delete" option from the "Trash" content list.
- disableBulkForceDelete: Removes "restore" from the bulk operations on the "Trash" content list.
- disableDelete: Removes the "delete" option from the content lists.
- disableBulkDelete: Removes the "delete" option from the bulk operations.
- disablePermalink: Removes the permalink from the create/edit screens.
- disableEditor: Removes the editor button from the edit page.
- disableBulkEdit: Disables bulk operations.
- disableIncludeScheduledInList: Hides publish scheduling information from the content list.
Enable defaults
- enableSkipCreateModal: Disables the create modal and directly forwards you to the full edit page.
- enableFeature: Allow to feature the content. This requires a 'featured' fillable boolean on the model.
- enableBulkFeature: Enables the "Feature" bulk operation.
- enableDuplicate: Enables the "Duplicate" option from the content lists.
- enableReorder: Allows to reorder the items, if this was setup on the model.
- enableEditInModal: Enables the function that content is edited in the create modal.
- enableShowImage: Shows the thumbnail of the content in the list.
Setters
-
setModuleName('
yourModuleName'): Set the name of the module you are working with. -
setFeatureField('
fieldname'): Set the field to use for featuring content. -
setSearchColumns(
['title', 'year']): Set the columns to search in. -
setSearchQuery(
fn (Builder $q, string $search) => $q->orWhereHas('profile', fn (Builder $q) => $q->where('first_name', 'like', "$search%")->orWhere('last_name', 'like', "$search%"))): For finer controller over the search -
setPermalinkBase('
example'): The static permalink base to your module. Defaults tosetModuleNamewhen empty. -
setTitleColumnKey('
title'): Sets the field to use as title, defaults totitle. -
setModelName('
Project'): Usually not required, but in case customization is needed you can use this method to set the name of the model this controller acts on. -
setResultsPerPAge(
20): Sets the amount of results to show per page, defaults to 20. -
setBreadcrumbs(
Breadcrumbs $breadcrumbs): Breadcrumbs to display. -
eagerLoadListingRelations(
['comments', 'author']): Relations to eager load for the index view. -
eagerLoadFormRelations(
['comments', 'author']): Relations to eager load for the form view. -
eagerLoadFormRelationCounts(
['comments', 'author']): Relation count to eager load for the form view.
Controller methods
There are a few methods that can be usefull to implement based on the needs of your application.
1/* 2 * Add anything you would like to have available in your module's index view (create modal) 3 */ 4protected function indexData($request) 5{ 6 return []; 7} 8 9/*10 * Add anything you would like to have available in your module's form view11 * For example, relationship lists for multiselect form fields12 */13protected function formData($request)14{15 return [];16}You can also override all actions and internal functions, checkout the ModuleController source
in A17\Twill\Http\Controllers\Admin\ModuleController.
Example: sorting by a relationship field
Let's say we have a controller with certain fields displayed:
File: app/Http/Controllers/Twill/PlayController.php
1protected $indexColumns = [ 2 'image' => [ 3 'thumb' => true, // image column 4 'variant' => [ 5 'role' => 'featured', 6 'crop' => 'default', 7 ], 8 ], 9 'title' => [ // field column10 'title' => 'Title',11 'field' => 'title',12 ],13 'festivals' => [ // relation column14 'title' => 'Festival',15 'sort' => true,16 'relationship' => 'festivals',17 'field' => 'title'18 ],19];To order by the relationship we need to overwrite the order method in the module's repository.
File: app/Repositories/PlayRepository.php
1... 2public function order($query, array $orders = []) { 3 4 if (array_key_exists('festivalsTitle', $orders)){ 5 $sort_method = $orders['festivalsTitle']; 6 // remove the unexisting column from the orders array 7 unset($orders['festivalsTitle']); 8 $query = $query->orderByFestival($sort_method); 9 }10 // don't forget to call the parent order function11 return parent::order($query, $orders);12}13...Then, add a custom sort scope to your model, it could be something like this:
File: app/Models/Play.php
1public function scopeOrderByFestival($query, $sort_method = 'ASC') {2 return $query3 ->leftJoin('festivals', 'plays.section_id', '=', 'festivals.id')4 ->select('plays.*', 'festivals.id', 'festivals.title')5 ->orderBy('festivals.title', $sort_method);6}Additional table actions
You can override the additionalTableActions() method to add custom actions in your module's listing view:
File: app/Http/Controllers/Twill/NewsletterController.php
1public function additionalTableActions() 2{ 3 return [ 4 'exportAction' => [ // Action name. 5 'name' => 'Export Newsletter List', // Button action title. 6 'variant' => 'primary', // Button style variant. Available variants; primary, secondary, action, editor, validate, aslink, aslink-grey, warning, ghost, outline, tertiary 7 'size' => 'small', // Button size. Available sizes; small 8 'link' => route('newsletter.export'), // Button action link. 9 'target' => '', // Leave it blank for self.10 'type' => 'a', // Leave it blank for "button".11 ]12 ];13}Localizing the permalink
In a multilingual setup it might be interesting to define a localized permalink base.
We saw before that we can customize the permalink using $permalinkBase but if we want to localize this we can use the controller method getLocalizedPermalinkBase.
1protected function getLocalizedPermalinkBase()2{3 return [4 'en' => 'page',5 'nl' => 'pagina',6 ];7}If you need more control or want to change the full permalink you can use the formData method instead.
The example below is a simple one and could be done as well with customizing the permalink
1protected function formData($request)2{3 return [4 'localizedCustomPermalink' => [5 'en' => route('page', ['id' => $request->route('page')]),6 'nl' => route('page', ['id' => $request->route('page')])7 ]8 ];9}Customizing the permalink
If needed you can customize the permalink displayed in the admin interface when editing a model. This is especially useful if you are using Laravel for displaying your front-end as you do not need to keep your permalink and routes in sync.
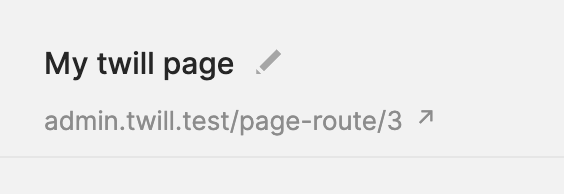
This can be done by setting the customPermalink via the formData method in the model controller.
The example below will result in: /page-route/3 for page with id 3.
1# Route definition 2Route::get('page-route/{id}', function() {...})->name('page.detail'); 3 4# Method implementation 5protected function formData($request) 6{ 7 if ($request->route('page')) { 8 return [ 9 'customPermalink' => route('page.detail', ['id' => $request->route('page')]),10 ];11 }12 return [];13}